As blockchain technology continues to evolve, a new model has emerged, promising to solve many issues that traditional blockchains cannot address. This is Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) – a potential technology in the cryptocurrency sector. In this article, we will explore “What is DAG Blockchain?” and delve into how it works, its advantages and disadvantages, and its practical applications in current cryptocurrency projects.
What is DAG Blockchain?
Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) is a data structure unlike traditional blockchain technologies. In a blockchain system, data is organized into blocks that are linked sequentially to form an immutable chain. However, DAG uses a directed graph model, where transactions are connected through nodes and edges, without requiring blocks.
DAG does not rely on the block concept as in blockchain. Instead, each new transaction in DAG must reference previous transactions to validate and authorize itself. This eliminates the need for creating blocks and removes the necessity for miners or validators to compete in finding new blocks, leading to faster processing times and reduced transaction costs.
Since DAG does not use blocks, it avoids the latency and congestion problems that traditional blockchains often face, particularly in systems that need to handle millions of transactions per second. Transactions in DAG can be processed in parallel without waiting for previous transactions to complete, enhancing scalability and transaction speed.
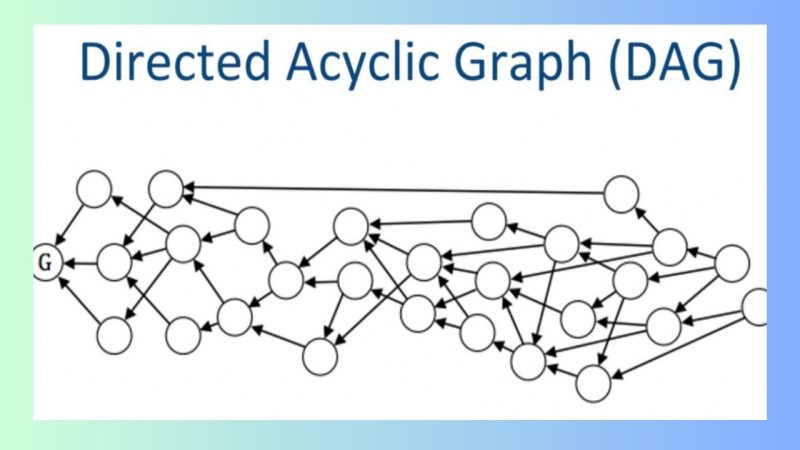
Structure and principles of DAG Blockchain
The structure of DAG is fundamentally different from a traditional blockchain system. Instead of organizing transactions into blocks, DAG uses a directed graph where the nodes represent transactions, and the edges represent the relationships between them. In a DAG system, there is no intermediary block containing transactions. New transactions must reference and validate older transactions before being added to the network.
The operation principle of DAG is simple yet effective. When a user creates a new transaction, it must reference at least two previous transactions to ensure its validity and confirmation. This process allows transactions within the DAG system to be validated simultaneously, eliminating the need to wait for the next block, as in blockchain systems.
This parallel validation process helps the DAG system avoid network congestion since there is no dependency on block time. While blockchain systems must wait for blocks to be added and validated, DAG transactions can be processed and confirmed concurrently, enabling the network to handle millions of transactions per second without congestion. Moreover, the absence of miners or validators creating new blocks reduces costs and saves energy across the system.
Comparing DAG Blockchain with traditional Blockchain
Although both DAG and blockchain are technologies for storing and validating transactions, they differ fundamentally in how transactions are organized and validated. In traditional blockchain systems, transactions are grouped into blocks, and these blocks are linked together into a chain, creating an immutable and secure link. However, this results in issues with speed and cost when processing a high volume of transactions.
In contrast, DAG organizes transactions in the form of a graph, without blocks and chains. Each new transaction is built upon previous transactions and confirmed concurrently. This removes the network congestion common in blockchain systems. Transactions in DAG are not limited by block time and can be validated instantly by referencing older transactions, making DAG an optimal solution for applications requiring high transaction speeds and large scalability.
Another important distinction is decentralization. Traditional blockchains are fully decentralized because every user in the network can participate in validating and creating new blocks. In contrast, DAG can be somewhat centralized, depending on the transaction validation mechanisms of specific DAG protocols.
Advantages of DAG Blockchain
DAG Blockchain offers several notable advantages, making it an attractive option for cryptocurrency applications and industries that require high transaction speed and low costs.

- High transaction speed: Unlike traditional blockchain, DAG is not limited by block time. This allows the system to process multiple transactions per second without congestion. Transactions can be validated simultaneously, reducing waiting times.
- Energy efficiency: One of DAG’s major benefits is its energy efficiency. Since it does not rely on energy-consuming consensus algorithms like Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS), DAG helps reduce operational costs and carbon emissions.
- No transaction fees: In some DAG systems, users can perform transactions without paying fees or with very low fees. This is particularly useful for microtransactions, such as small payments or IoT applications.
- Scalability: DAG offers superior scalability compared to traditional blockchain since it is not limited by block time. This allows the system to handle millions of transactions per second without congestion, making it ideal for applications that demand high speed and scalability.
Limitations of DAG Blockchain
Despite its many advantages, DAG technology still has some limitations that need to be addressed.
- Not fully decentralized: One weakness of DAG is centralization in some protocols. Since there are no blocks and the validation process may be controlled by a few key nodes, DAG does not achieve the full decentralization that traditional blockchain systems offer.
- Vulnerable to spam attacks: With transaction fees being nearly zero or very low, DAG systems are susceptible to spam attacks. Malicious actors can send a large number of invalid transactions to clog the network, making it unstable.
- Limited applications: While DAG has many benefits, it is still under development and cannot fully replace blockchain in applications requiring high security, such as finance or banking. Its applications in cryptocurrency are still limited, and the technology needs further improvement before it can become widely adopted.

DAG Blockchain applications in cryptocurrency
DAG Blockchain has already been implemented in some prominent cryptocurrency projects, particularly in Internet of Things (IoT) applications, where high transaction speeds and low costs are essential.
IOTA: A Pioneer in Internet of Things (IoT)
IOTA uses the DAG architecture (Tangle) to process transactions in IoT environments. Unlike traditional blockchain, IOTA has no transaction fees and is not limited by block time, enabling fast and low-cost transactions. This is especially useful in IoT applications, where millions of small transactions need to be processed daily without network congestion.
Nano: Fee-free cryptocurrency
Nano employs a block-lattice system combined with DAG, allowing each user to have their own blockchain. Transactions are processed instantly and without fees, making Nano an ideal choice for fast and low-cost transactions, particularly in micro-payments or IoT applications.
U2U Chain: Enhancing speed and scalability
U2U Chain, part of the U2U Network, uses DAG to address transaction speed and cost issues. The DAG technology in U2U Chain facilitates the processing of millions of transactions per second without network congestion, making it suitable for DePIN and IoT applications. The subnet model also enhances the scalability and security of the system.
DAG Blockchain is a promising technology in the cryptocurrency industry and other fields, particularly for applications requiring high transaction speeds and low costs. While it still has limitations and is under development, DAG promises to solve the issues traditional blockchain faces, from fast transaction processing to reduced operational costs and improved scalability. However, for DAG to become the main choice for real-world applications, the technology needs to continue evolving and improving.
This article from Digital Economy Pulse has provided an in-depth explanation of the term “What is DAG Blockchain?” We hope the knowledge shared helps you gain a comprehensive understanding of this new technology when selecting investment projects. Best of luck!